Thursday, April 6, 2023
Car Stolen by Hacking IoT Devices
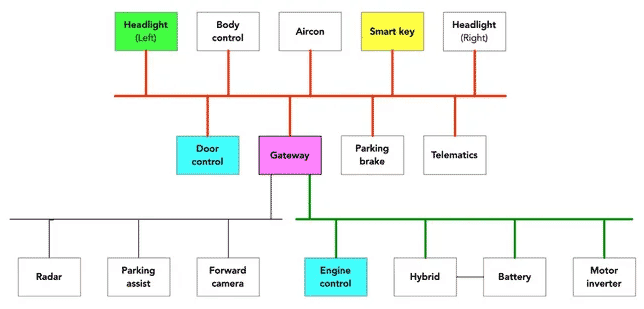
Recently criminals managed to hack into a sophisticated vehicle control system connected to the internet of things (IoT) through the headlights. The control system is managed by a controller area network (CAN), an IoT protocol that allows devices and microcontrollers in a car to communicate with each other.
By manipulating the electronic control unit (ECU) in the Toyota RAV4 headlights. Once connected via the headlights, an attacker can gain access to the CAN bus, which is responsible for functions such as the parking brake, headlights and smart locks, and then to the powertrain panel where the engine controls are located.
While hacking high-end cars is nothing new, this attack method highlights the vulnerabilities in the IoT protocol, necessitating greater security measures in automotive systems. This incident will force manufacturers to improve the security of their vehicle networks.
Cow Manure Is Processed Into Biogas Energy
Cow Manure Is Processed Into Biogas Energy
Livestock manure is commonly used as fertilizer. However, recently dairy farms in New England are experimenting with converting cow manure into energy by burning the biogas found in cow dung. This is because in cow dung there are microorganisms that can break down organic matter into methane.
On the Massachusetts dairy farm, there is a 550,000-gallon underground tank capable of processing about 9,000 tons of cow manure per year. This oxygen-free tank mixes sewage waste at temperatures of 95 and 105 degrees Fahrenheit, and further encourages bacteria to feed on carbon, nitrogen, and other organic matter.
This process is known as anaerobic digestion, where methane is finally produced. Next, through a network of pipes, the gas is then directed to a special engine that burns methane to produce heat and electricity. The remaining organic matter that cannot be digested after the anaerobic process can still be used for agricultural purposes.
Read more:
Smithsonianmag
On the Massachusetts dairy farm, there is a 550,000-gallon underground tank capable of processing about 9,000 tons of cow manure per year. This oxygen-free tank mixes sewage waste at temperatures of 95 and 105 degrees Fahrenheit, and further encourages bacteria to feed on carbon, nitrogen, and other organic matter.
This process is known as anaerobic digestion, where methane is finally produced. Next, through a network of pipes, the gas is then directed to a special engine that burns methane to produce heat and electricity. The remaining organic matter that cannot be digested after the anaerobic process can still be used for agricultural purposes.
Read more:
Smithsonianmag
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)